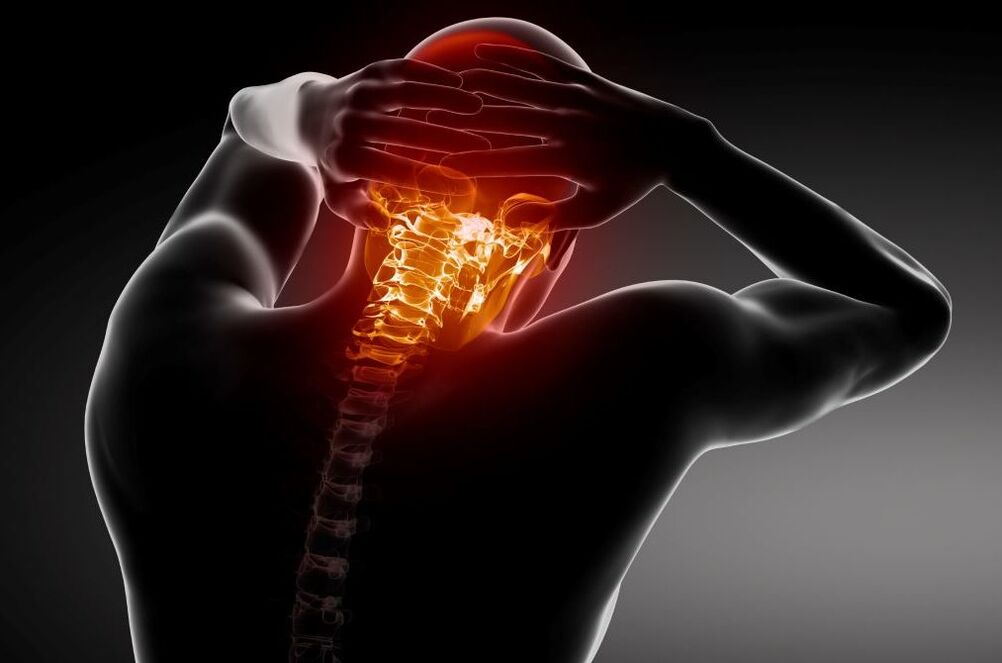
Depending on the localization of the lesion of the spinal column, each department is characterized by its own symptoms of osteochondrosis. Some of them are connected directly with the structures of the spine, the other part - with a violation of the innervation of those organs and structures that belong to the affected section. Symptoms typical of cervical osteochondrosis. belong to several groups or syndromes:
- vertebrogenic;
- vertebral artery;
- cardiac;
- radicular.
Vertebrogenic syndrome in cervical osteochondrosis
Due to changes in the bone and cartilage tissues of the spine in osteochondrosis. Violation of mobility in the joints of the spinal column, a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae lead to their deformation and restriction of movement in the cervical region.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs are not necessarily associated with age, they can be the result of excessive load, poor posture, etc. , which is especially evident in the cervical spine. Cervical osteochondrosis occurs as a result of such causes, even at a young age.
Changes in the tissues can be reversible, however, morphological signs in osteochondrosis are always present and are diagnosed radiologically: dehydration, shrinkage and degeneration of the intervertebral discs.
With the aggravation of the process - the formation of bone growths on the vertebrae. Vertebrogenic syndrome is the main one in any form of osteochondrosis. Its manifestations in the cervical region:
- Violation of the mobility of the cervical spine;
- Pain when turning or tilting the head;
- Changes in the structures of the spine (body and discs).
During an exacerbation of the process of pain in the cervical region (cervicalgia), they are also disturbed in a state of immobility. It is characteristic that the pain radiates to the occipital region of the head (cervicocranialgia), sometimes spreads to the entire head, becomes intense, unbearable.
vertebral artery syndrome

Compression of the vertebral artery as a result of degenerative processes in the spinal column (or tissue edema during periods of exacerbation) is manifested by impaired blood flow and symptoms of hypoxia in the brain. Dizziness, nausea and vomiting, changes in total arterial and intracranial pressure, tinnitus, lethargy and impaired coordination are noted.
Not only mechanical compression as a result of osteochondrosis of the cervical region, but also irritation of the walls of the artery, their nerve endings contribute to the manifestation of specific symptoms.
Intense headaches of the migraine type, fainting with sharp turns of the head are typical manifestations of the vertebral artery syndrome in cervical osteochondrosis.
Cardiac syndrome
Compression of the nerve roots of the cervical region, reflex spasms of blood vessels as a result of osteochondrosis give manifestations in the region of the heart. Cardiac syndrome is manifested by pain in the sternum, palpitations, weakness, a feeling of lack of air. With exacerbations of osteochondrosis, cardiac syndrome can be combined with jumps in blood pressure.
radicular syndrome
Compression of the nerve roots emerging from the cervical spine is manifested by movement disorders (paralysis, semi-paralysis) and sensitivity in the areas that they innervate.
Signs of conduction disorders in cervical osteochondrosis:
- 1-2 pairs of roots: headache in the back of the head, numbness or increased sensitivity;
- 3-4 pair of roots: localization of pain and sensory disturbances in the pharynx (tongue), larynx (hiccups, difficulty swallowing), throat, ears;
- 5-6 pair of roots: pain and movement disorders in the arms, shoulders, shoulder blades;
- 7 pair of roots: the lesion causes impaired movement and numbness of the fingers - middle and index, 8 pair - ring and little fingers.
Confirmation of the diagnosis
A variety of symptoms in cervical osteochondrosis is associated with the impact of the process on the nerve roots and trunks, which will result in sensory disturbances, motor function, pain and circulatory disorders of the innervated zones.
Difficulties in diagnosis arise if the patient has symptoms of hypertension, cardiac disorders and neurological symptoms, which may mask a stroke or transient cerebral ischemia.
Sudden loss of consciousness can be both a sign of osteochondrosis with vertebral artery syndrome, and acute cerebrovascular accident. Paleness, weakness, tachycardia accompanying the condition are possible in both cases, as reactions of the autonomic system.
Another syndrome in cervical osteochondrosis, which requires close differential diagnosis, is cardiac. Equally important is the identification of the dependence of blood pressure surges on osteochondrosis.
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, the examination plan for cervical osteochondrosis includes:
- X-ray examination of the spine;
- CT and MRI of the spine and brain;
- Electrocardiography and ultrasound of the heart;
- Holter AD;
- General blood analysis.
The intensity of the manifestation of symptoms during periods of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis may require not only an extended examination, but also hospitalization in case of suspicion of the danger of emergency conditions: acute neurological or cardiological pathology.


















